3D printing enables you to quickly and cost-effectively prototype and manufacture parts for a variety of applications. But choosing the right 3D printing process is only one part of the equation. Ultimately, it depends a lot on the material, enabling you to create parts with the desired mechanical properties, functional properties or appearance.
Plastic:
There are dozens of plastic materials available for 3D printing, each with unique qualities that make them best for specific use cases.
|
Material
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
Hardware Requirements
|
|
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
|
-
Impact- resistant
-
Wear-resistant
-
Low cost
|
-
Difficult to print due to warping and poor bed adhesion
|
Standard FDM printer, heated enclosure recommended
|
|
PP (Polypropylene )
|
-
Impact-resistant
-
Fatigue resistant
-
Good surface finish
-
Good chemical resistance
|
-
Difficult to print due to warping and poor bed adhesion
|
May require nonstandard bed covers for adhesion
|
|
PC (Polycarbonate)
|
-
One of the strongest 3D printer filaments
-
Transparent
|
-
Difficult to print
-
High cost
|
FDM printer capable of printing at very high temperatures
|
|
PVA (Polyvinyl Alcohol)
|
|
-
Can only be used for support material
|
Standard FDM printer
|
POWDERES:
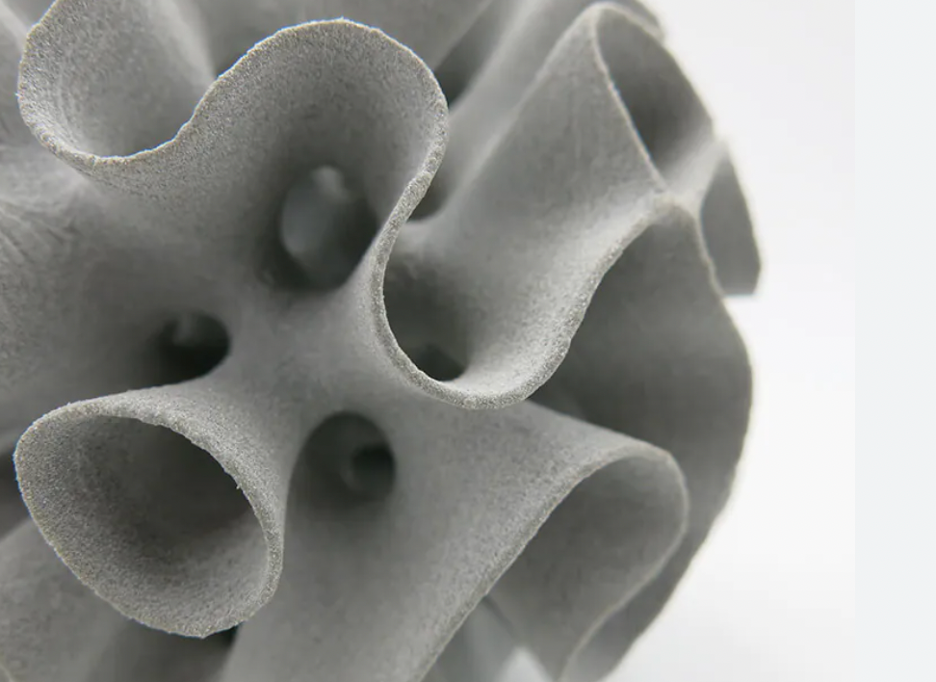

Today's more advanced 3D printers use powdered materials to create products. Inside the printer, the powder is melted and spread in layers until the desired thickness, texture and pattern is achieved. Powders come in a variety of sources and materials, but the most common are:
1.Polyamide(Nylon): Nylon is an engineering thermoplastic used in many mechanical applications such as rings or various pulleys, it has a coefficient of friction as well as good temperature and chemical resistance. Nylon is difficult to stick to building boards due to its low coefficient of friction. It has a high melting point and tends to absorb moisture, but after a successful start, it prints well due to its excellent bonding properties.
2. Aluminide: Composed of a mixture of aluminum and gray polyamide, aluminized powder is used to produce some of the strongest 3D printed models. Known for its grainy and sandy appearance, the powder can be used for industrial models and prototypes.
RESINS:
1.High Detail Resin: Usually used for small models that require intricate details.
2. Paintable resins: Sometimes used for 3D printing with smooth surfaces, these resins are known for their aesthetic appeal.
3. Transparent Resin: This is the strongest class of resin and therefore best suited for a range of 3D printed products. Typically used for models that must have a soft touch and a transparent look.
METAL:
Metal 3D printing (or metal additive manufacturing) quickly creates functional prototypes using the same materials as final production components. The technology could also reduce the cost and time of manufacturing specialized metal parts for high-tech fields such as aerospace and industrial equipment.
•Stainless steel
•aluminum
•titanium
•nickel
GRAPHITE AND GRAPHENE
Graphene has become a popular choice for 3D printing due to its strength and electrical conductivity. The material is ideal for equipment parts that require flexibility. Graphene is also used in solar panels and components.