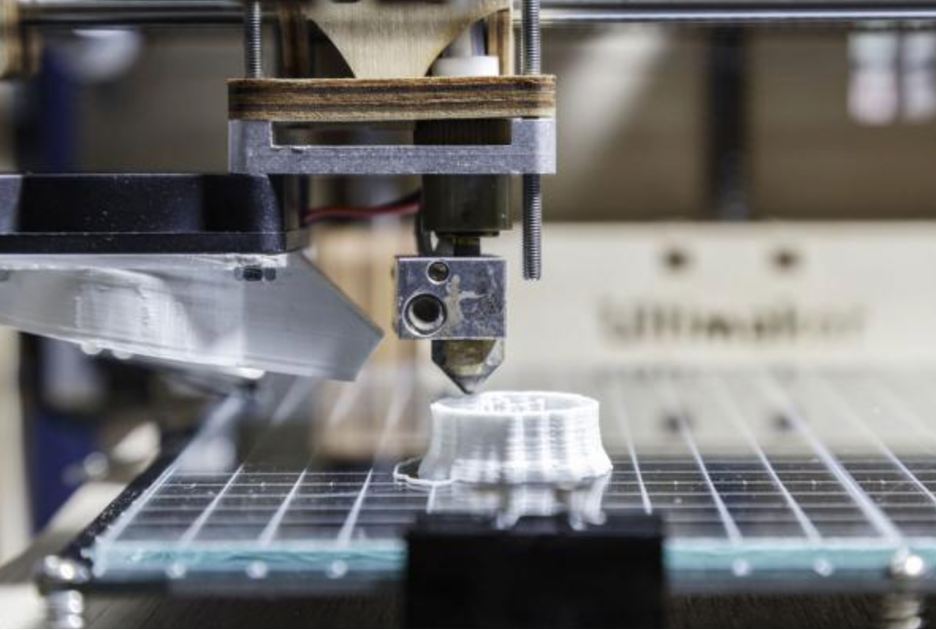
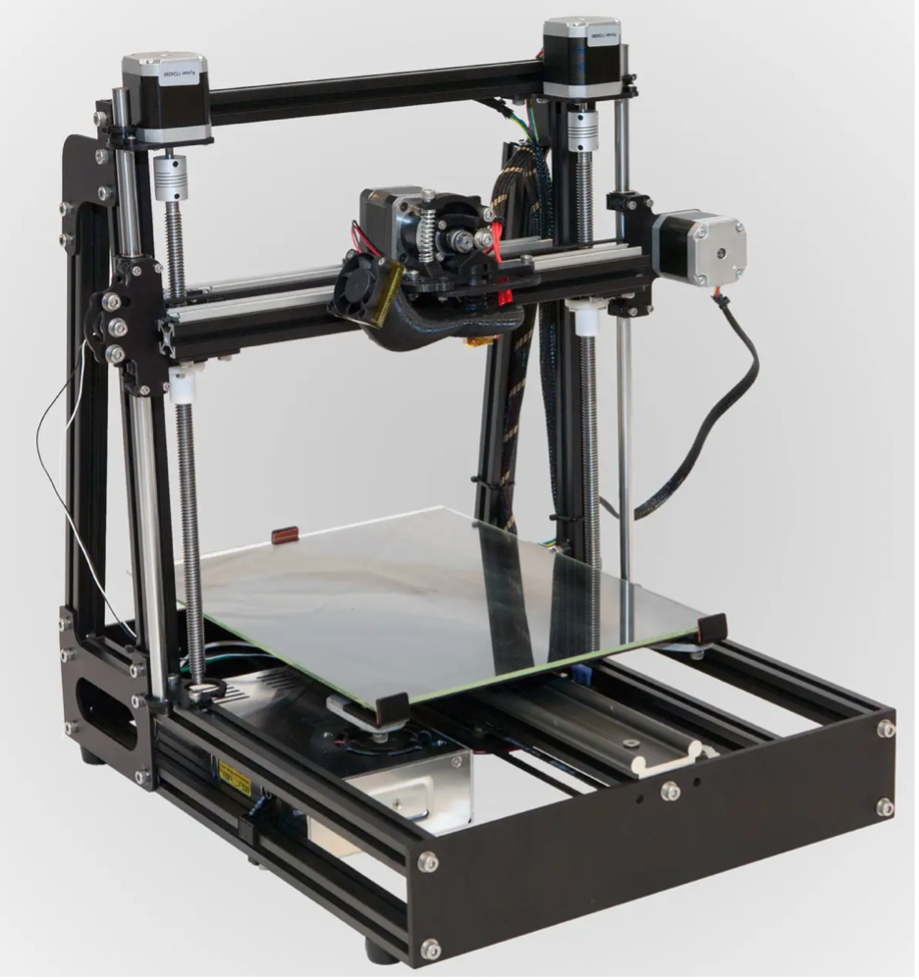
- +86 760 8996 2989
- enquiry@nice-rapidtooling.com
shownav
hidnav
- Services
- Rapid Aluminium Tooling
- SLA Rapid Prototypes Machine
- CNC Molding and CNC Milling Services in China
- Injection Moulding Price China
- SLA 3D Printing Service
- Low Volume Production
- FDM 3D Printing Service China
- CNC Parts Machining Supplier China
- Silicone Compression Molding
- Die Casting Mould
- Small Batch CNC Machining
- Finishing Services
- Resources
- News And Blogs
- About us
- Contact
- Request a Quote